DevExpress Office File API是一个专为C#, VB.NET 和 ASP.NET等开发人员提供的非可视化.NET库。有了这个库,不用安装Microsoft Office,就可以完全自动处理Excel、Word等文档。开发人员使用一个非常易于操作的API就可以生成XLS, XLSx, DOC, DOCx, RTF, CSV 和 Snap Report等企业级文件。
在之前两篇与AI相关的博客中,我们了解了如何使用DevExpress Office File API库和Azure AI OpenAI服务为Word和Excel文档中使用的图像、图表和超链接生成可访问的描述:
- DevExpress Office File API中文教程 - 如何用OpenAI模型增强Office文档可访问性?
- 界面组件DevExpress Office File API - 如何用OpenAI增强文档可访问性?
在这篇文章中,我们将详细介绍另一个易于访问的文档生成重要技巧——在多语言的Word文档中检测和设置段落的校对语言。此外,我们还将描述如何翻译多语言文档,以及如何生成可访问的注释,并将段落翻译为所选语言。
DevExpress技术交流群10:532598169 欢迎一起进群讨论
在生成可访问的Word文档(特别是多语言文档)时,必须指定证明语言并为文本段落添加翻译,这有几个原因。语言设置帮助屏幕阅读器解释和发音文本,辅助功能和工具(如拼写/语法检查器)依赖于这些设置来提供准确的建议和更正。在将Word文档导出为可访问的PDF格式时,语言设置也很重要。带有段落翻译的注释有助于增加文档内容的清晰度,有助于文档的可访问性,并增强多语言环境中的协作。
为了满足这些特殊需求,我们将使用DevExpress Word Processing Document和两个Azure人工智能服务——语言和翻译。请在GitHub上的示例项目中查看这些功能的新端点:Office File API – Integrate AI。
在将此解决方案合并到您的应用程序之前,请务必阅读并理解Azure AI服务的使用条款和条件。
实现细节
使用Azure AI语言API
Azure AI语言服务需要Azure订阅,订阅后,在Azure门户网站中创建语言资源来获取密钥和端点。
注意:您可以创建多服务资源来访问具有相同密钥和端点的多个AI服务。
安装Azure.AI.TextAnalytics NuGet包到您的项目中,使用语言服务API进行文本语言检测。下面的代码片段对TextAnalyticsClient进行身份验证,向服务发送文本,服务返回有关检测到的语言的信息。对于这个实现,我们只需要“ISO 693-1”格式的语言名称。
public class AzureAILanguageHelper
{
private TextAnalyticsClient client;
internal AzureAILanguageHelper(string key, Uri endpoint)
{
AzureKeyCredential azureCredential = new AzureKeyCredential(key);
client = new TextAnalyticsClient(endpoint, azureCredential);
}
internal async Task<string> DetectTextLanguage(string text)
{
DetectedLanguage detectedLanguage = await client.DetectLanguageAsync(text);
return detectedLanguage.Iso6391Name.Replace('_', '-');
}
}
使用Azure AI Translator API
就像语言服务一样,Azure AI Translator也需要Azure订阅,您需要在Azure门户网站中创建Translator资源(或使用多服务资源)。
安装Azure.AI.Translation.Text NuGet包到您的项目中,并验证TextTranslationClient。
注意:如果使用Azure AI多服务或区域转换器资源,必须指定“region”参数用于客户端身份验证。
下面的代码片段发送文本/目标语言名称(采用“ISO 693-1”格式),并获得翻译后的内容作为响应。
public class AzureAITranslationHelper
{
TextTranslationClient client;
internal AzureAITranslationHelper(string key, Uri endpoint, string region = "global")
{
AzureKeyCredential azureCredential = new AzureKeyCredential(key);
client = new TextTranslationClient(azureCredential, endpoint, region);
}
internal async Task<string> TranslateText(string text, string sourceLanguage, string targetLanguage)
{
Response<IReadOnlyList<TranslatedTextItem>> response = await client.TranslateAsync(targetLanguage, text, sourceLanguage);
TranslatedTextItem translatedTextItem = response.Value.First();
return translatedTextItem.Translations[0].Text;
}
}
实现Word Processing Document API API端点
要在DevExpress驱动的Word Processing Document API应用程序中使用上面的API,请在RichEditDocumentServer实例中加载文档,并遍历Document.Paragraphs集合。使用Document.GetText方法获取段落文本,使用Document.BeginUpdateCharacters 方法访问段落字符属性。检查段落文本和字符设置 - 如果段落文本不为空并且语言设置(CharacterProperties.Language)未指定,则调用azureaillanguagehelper。DetectTextLanguage方法检测段落语言。完成后,将检测到的语言作为CultureInfo对象分配给CharacterProperties.Language属性,并使用Document.EndUpdateCharacters方法完成段落编辑。如果检测到的语言不同于默认文档语言(在当前示例中,我们假设默认语言是英语),则使用AzureAITranslationHelper.TranslateText方法将段落文本翻译为所需的语言。此时,您可以向当前段落添加注释,并在该注释中插入翻译后的文本。
public async Task<IActionResult> GenerateLanguageSettingsForParagraphs
(IFormFile documentWithHyperlinks,
[FromQuery] RichEditFormat outputFormat) {
try {
var languageHelper =
new AzureAILanguageHelper(languageAzureKey, languageEndPoint);
var translationHelper =
new AzureAITranslationHelper(translationAzureKey, translationEndPoint);
using (var server = new RichEditDocumentServer())
{
await RichEditHelper.LoadFile(server, documentWithHyperlinks);
server.IterateSubDocuments(async (document) =>
{
foreach (var paragraph in document.Paragraphs)
{
CharacterProperties cp =
document.BeginUpdateCharacters(paragraph.Range);
string paragraphText =
document.GetText(paragraph.Range);
if (cp.Language.Value.Latin ==
null && !string.IsNullOrWhiteSpace(paragraphText))
{
CultureInfo? culture = null;
string language =
languageHelper.DetectTextLanguage(paragraphText).Result;
try { culture = new CultureInfo((language)); }
catch { }
finally
{
if (culture != null)
{
// Set the paragraph language
cp.Language =
new DevExpress.XtraRichEdit.Model.LangInfo(culture, null, null);
if (language != "en")
{
// Generate an accessible comment with the paragraph translation
Comment comment =
document.Comments.Create(paragraph.Range, "Translator");
SubDocument commentDoc = comment.BeginUpdate();
string translatedText =
translationHelper.TranslateText(paragraphText, language, "en").Result;
commentDoc.InsertText(commentDoc.Range.Start,
$"Detected Language: {language}\r\nTranslation (en): {translatedText}");
comment.EndUpdate(commentDoc);
}
}
}
}
document.EndUpdateCharacters(cp);
}
});
Stream result =
RichEditHelper.SaveDocument(server, outputFormat);
string contentType =
RichEditHelper.GetContentType(outputFormat);
string outputStringFormat =
outputFormat.ToString().ToLower();
return File(result, contentType, $"result.{outputStringFormat}");
}
}
catch (Exception e)
{
return StatusCode(500, e.Message + Environment.NewLine + e.StackTrace);
}
}
检查输出
输出的Word文件将包括每个非空文档段落的语言设置(可在Language对话框中查看),以及每个非英语文本段落的相应翻译注释。
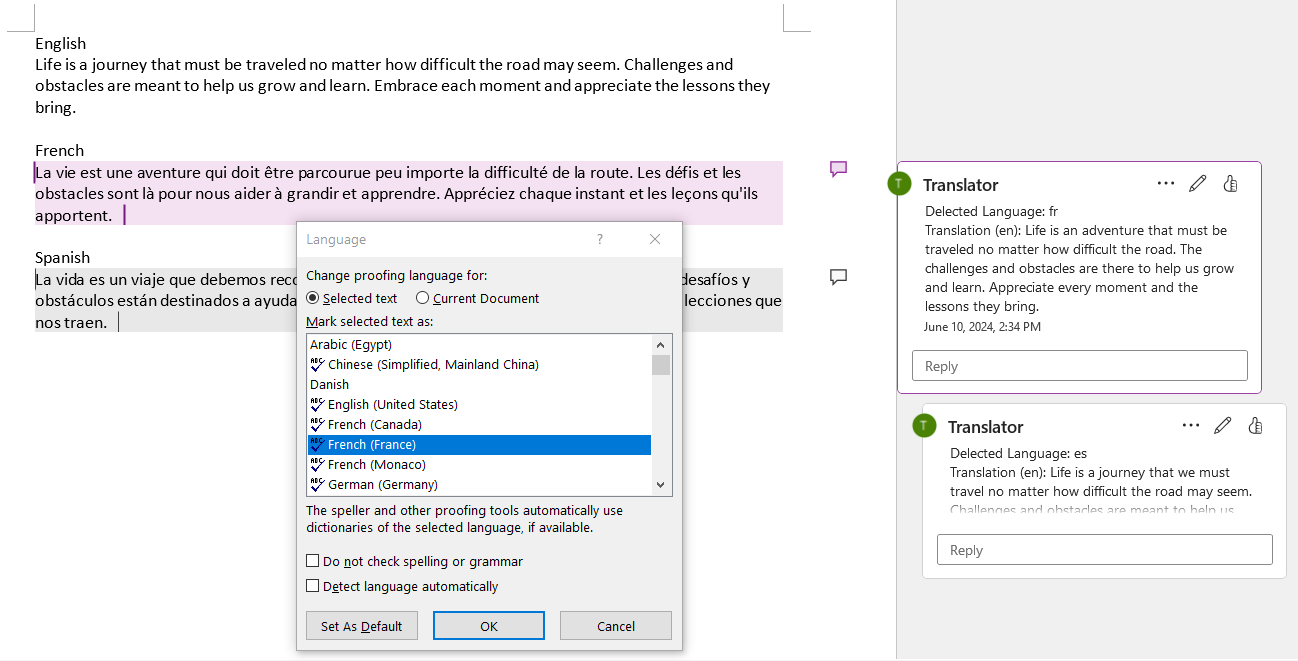
更多DevExpress线上公开课、中文教程资讯请上中文网获取

欢迎任何形式的转载,但请务必注明出处,尊重他人劳动成果
转载请注明:文章转载自:DevExpress控件中文网 [https://www.devexpresscn.com/]
本文地址:https://www.devexpresscn.com/post/4716.html

 联系电话:023-68661681
联系电话:023-68661681





 返回
返回